
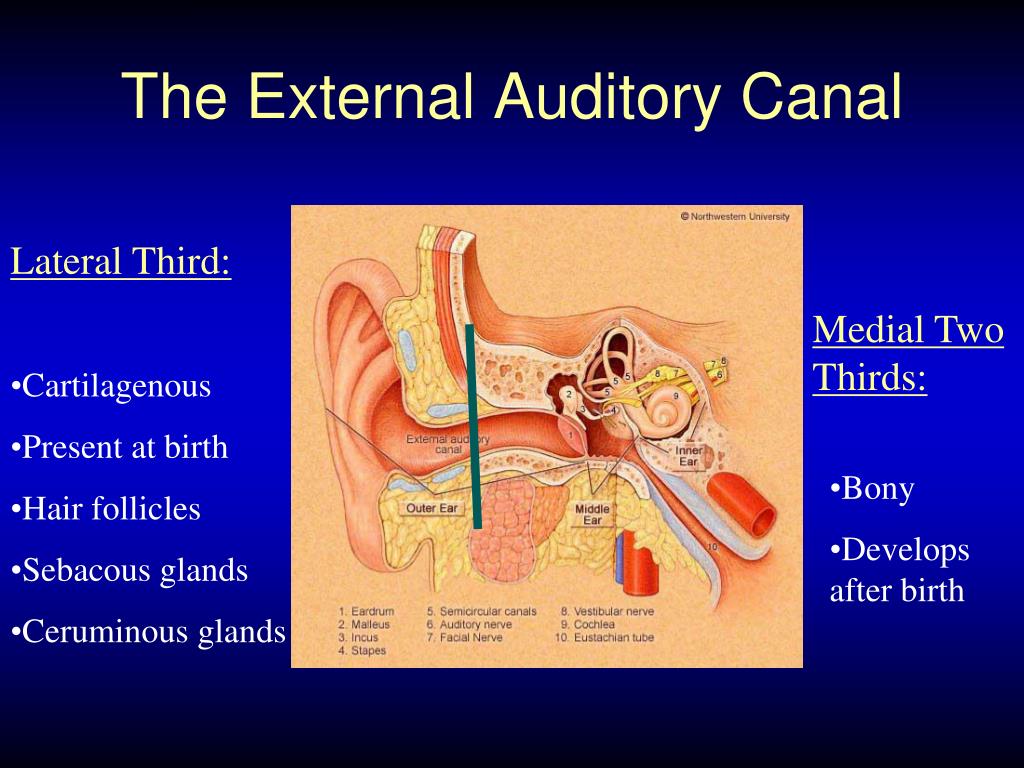
The pinna is a fibrocartilaginous structure with hillocks and recesses, among them. Terminology As the term external auditory meatus is variably used to refer to the canal its. The external ear consists of the pinna and the external auditory canal (EAC).

After 3 months, the patient presented with severe bilateral otalgia associated with. A normal variant defect in the anteroinferior aspect of the osseous part of the canal that connects with the temporomandibular joint is known as the foramen tympanicum (foramen of Huschke). The external auditory canal (EAC) or external auditory meatus (EAM) extends from the lateral porus acusticus externus medially to the tympanic membrane. (C) Contrast abdominal CT showing the tumor in the left kidney.
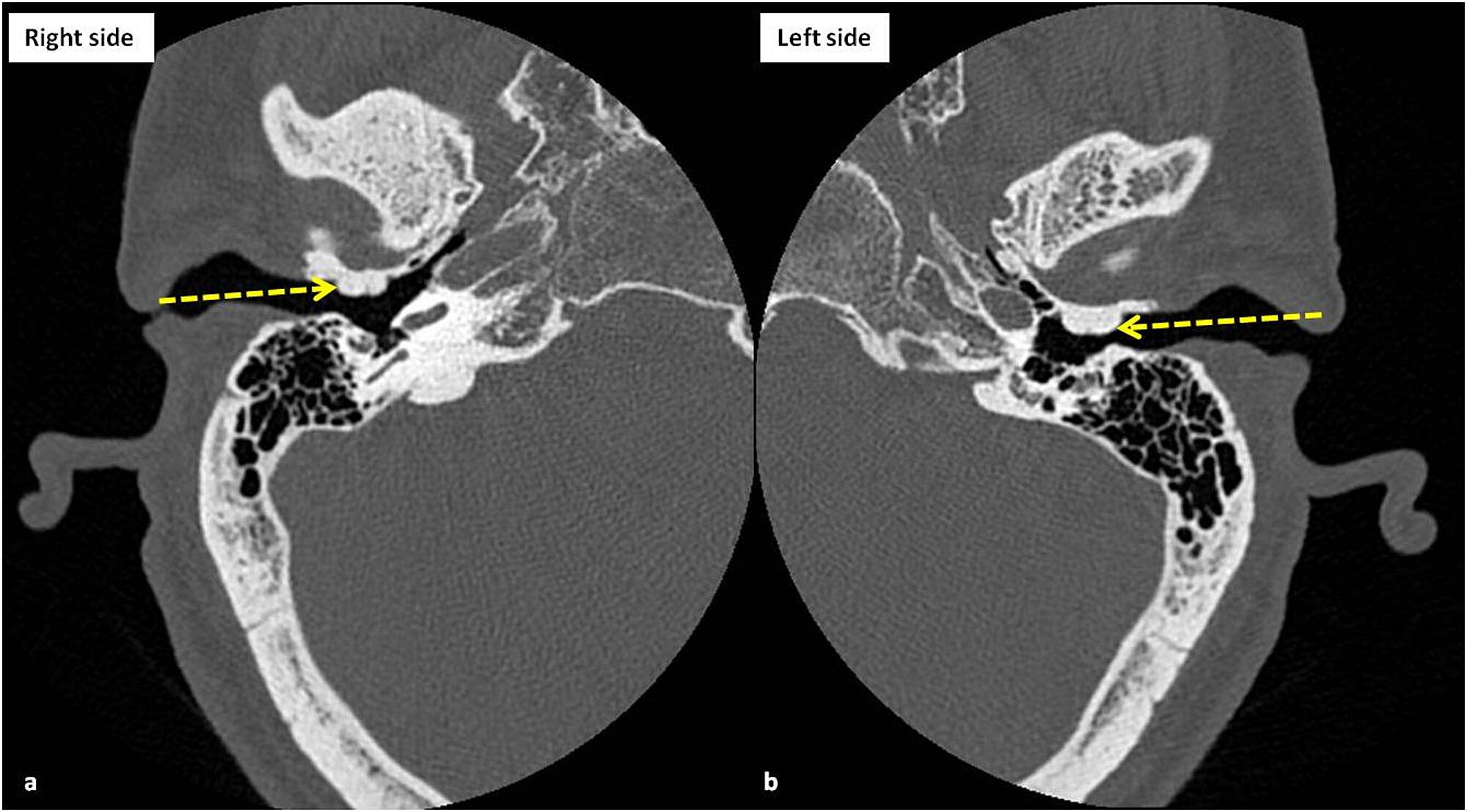
#LEFT EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL SKIN#
The skin of this inner part is directly applied to periosteum, with no subcutaneous tissue present. The roof and upper part of the posterior wall arise from the squamous part of the temporal bone 4. High-resolution CT is well suited for the evaluation of the temporal bone, which has a complex anatomy with multiple small structures. Dermatitis can be caused by exposure to allergens (contact dermatitis) or can be spontaneous (chronic otitis externa, aural eczematoid dermatitis). Congenital, inflammatory, neoplastic, and traumatic lesions can affect the EAC. Dermatitis of the ear canal is characterized by pruritis, scaling, flaking, and erythema of the skin of the external auditory meatus and ear canal. The ear canal is a narrow, tube-like structure that extends from the outer ear to the eardrum. On the left bilateral bony lesions of the external auditory canal, typical of exostoses. The anterior wall, floor, and lower part of the posterior wall arise from the tympanic part of the temporal bone 3,4. The external auditory canal is an S- shaped osseo-cartilaginous structure that extends from the auricle to the tympanic membrane. The inner ear includes the cochlea and semicircular canals. Computed tomography (CT) temporal bone demonstrated soft tissue density in the left EAC. The medial two-thirds is surrounded by bone. The patient was having moderate conductive hearing loss on audiometry. The white mass in the left external auditory canal, which easily separated from the tympanosquamous fissure of the temporal bone, was excised with a Rosen.
Defects in the cartilaginous part of the canal, which allow transmission of infection and malignancy, are known as fissures of Santorini. The lateral one-third is bounded by a fibrocartilaginous tube continuous with the auricle 3. The external auditory canal is typically 2.5 cm in length and is S-shaped. As the term external auditory meatus is variably used to refer to the canal itself or the porus acusticus externus (the round lateral opening), it may be better to use the term external auditory canal rather than meatus to avoid potential confusion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
